Secure Digital Evidence Management: Chain of Custody & Automated Redaction
by Ali Rind, Last updated: January 19, 2026, ref:

Digital evidence rarely fails because it is missing. It fails because it cannot be defended. When evidence is challenged in court, during an audit, or under public scrutiny, the question is not whether the file exists, but whether its handling can be proven and its integrity trusted.
For public safety agencies, gaps in chain of custody weaken cases and undermine transparency. For legal and compliance teams, inconsistent or manual redaction creates risk during discovery and regulatory review. In regulated industries, the inability to demonstrate evidence integrity and privacy controls can lead to audit findings, penalties, or reputational damage.
Secure digital evidence management must be built around defensibility, not convenience. Two capabilities determine whether evidence can be trusted at scale: an unbroken chain of custody that documents every interaction, and automated redaction that protects sensitive information while remaining auditable. This use-case deep dive examines how these controls form compliant, defensible evidence workflows from ingestion through disclosure.
Why Chain of Custody is Central to Digital Evidence Management
Chain of custody refers to the documented history of evidence from the moment it is created or collected through every access, transfer, and use. In digital environments, this concept becomes even more important because files can be copied or altered without visible signs of tampering if controls are weak.
For public safety agencies, a broken chain of custody can undermine investigations and weaken cases in court. For legal and compliance teams, it creates risk during audits, discovery, and regulatory reviews. In regulated industries, it can lead to questions about data integrity and governance.
A defensible digital chain of custody must:
- Establish evidence authenticity at ingestion
- Prevent unauthorized modification or deletion
- Track every interaction with the evidence
- Preserve original files alongside derived versions
- Provide verifiable records for audits and legal review
Without these controls, evidence credibility can be challenged, regardless of its content.
Secure Evidence Ingestion as the Starting Point
Chain of custody begins at ingestion. Whether evidence is captured directly from a device or uploaded from an external source, the system must immediately establish trust.
Secure ingestion practices include:
- Encrypted transfer and storage of evidence files
- Automatic capture of metadata such as date, time, source, and uploader identity
- Generation of cryptographic hashes to verify file integrity
- Role-based access controls applied from the start
By automating these steps, organizations reduce reliance on manual handling and ensure that evidence origin and integrity are documented consistently.
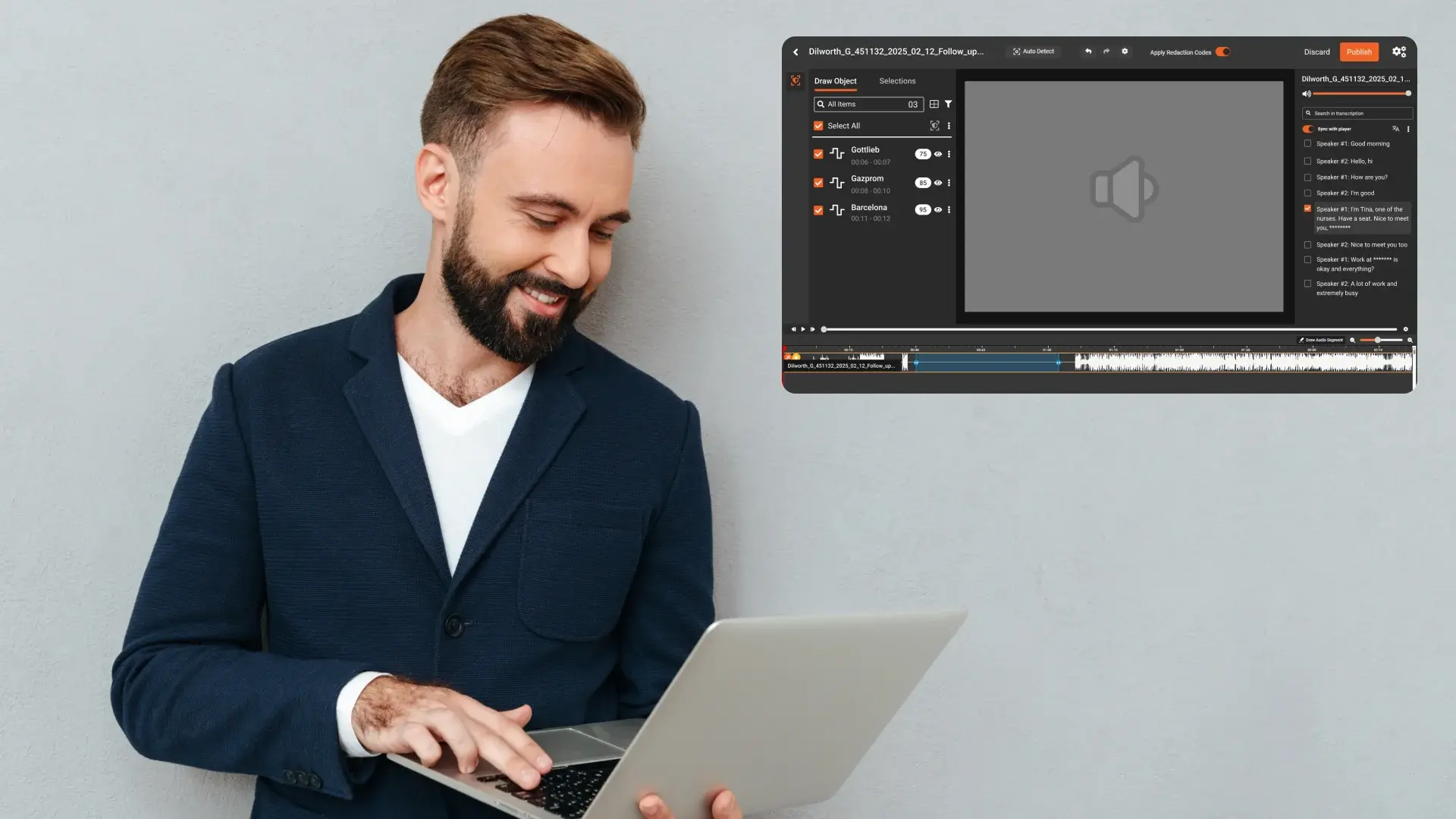
Automated Redaction as a Compliance Requirement
Digital evidence frequently contains sensitive or protected information. Faces of bystanders, license plates, personal identifiers, and confidential conversations are common across video and audio recordings. Releasing or sharing such evidence without proper redaction can violate privacy laws and internal policies.
Manual redaction is time-consuming, costly, and prone to error. As evidence volumes grow, it becomes unsustainable.
Automated redaction uses AI-driven detection to identify and protect sensitive content at scale. Typical redaction targets include:
- Faces of bystanders, witnesses, or minors
- License plates and vehicle identifiers
- Screens, documents, and visible credentials
- Spoken or visible personal identifiers
From a compliance standpoint, automated redaction supports privacy regulations and disclosure obligations while significantly reducing the risk of accidental exposure.
Making Automated Redaction Defensible
Automation alone is not enough. Redaction must be transparent and auditable to be defensible.
A compliant redaction workflow should record:
- What elements were redacted
- When redaction occurred
- Which rules or detection models were applied
- Who reviewed and approved the redacted output
This auditability is critical when evidence is challenged in court or reviewed by regulators. It allows organizations to demonstrate that redaction decisions were consistent, intentional, and policy-driven.
Preserving Chain of Custody Across the Evidence Lifecycle
Chain of custody does not end after ingestion or redaction. It must be maintained throughout the entire evidence lifecycle.
A secure digital evidence management system enforces continuous chain of custody by:
- Logging every access, view, edit, export, and share
- Preventing silent overwrites or deletions
- Preserving immutable originals alongside redacted or clipped versions
- Recording user identities, timestamps, and action details
These controls ensure that evidence integrity can be proven at any point, even years after collection.
Tamper-Proof Audit Trails and Accountability
Audit trails provide the accountability layer that ties chain of custody and redaction together. They create a chronological record of all actions taken on evidence and are essential for compliance and legal defensibility.
Effective audit trails should be:
- Automatically generated
- Protected from alteration or deletion
- Comprehensive across administrative and user actions
- Searchable and exportable for audits and litigation
For legal, compliance, and oversight teams, audit trails are often the primary mechanism used to validate evidence handling practices.
How Compliance Requirements Translate Into Evidence Workflows
Across regulated sectors, compliance expectations are consistent even when use cases differ.
-
Public safety agencies require transparent chain of custody, automated redaction for public disclosure, and defensible audit trails.
-
Legal and compliance teams need evidence integrity, access controls, retention enforcement, and audit readiness.
-
Regulated enterprises must protect sensitive data while meeting regulatory, contractual, and governance requirements.
Secure digital evidence management workflows address these needs by embedding compliance into daily operations rather than relying on policy enforcement alone.
Platforms such as the VIDIZMO Digital Evidence Management System embed compliance directly into digital evidence workflows by unifying secure ingestion, chain of custody, automated redaction, and audit trails. This allows organizations to manage digital evidence consistently and defend its integrity under legal and regulatory scrutiny.
If you are evaluating how to strengthen digital evidence defensibility, connect with our team to see how VIDIZMO Digital Evidence Management System supports secure, compliant evidence workflows.
Key Takeaways
-
Defensibility, not availability, determines evidence value.
Digital evidence must be provably handled, protected, and preserved to remain credible under scrutiny. -
Chain of custody is foundational to digital evidence management.
A complete, documented record of every interaction is essential to maintain integrity and legal admissibility. -
Automated redaction is a compliance requirement, not a convenience.
At scale, only automated and auditable redaction can consistently protect sensitive information and meet disclosure obligations. -
Audit trails connect custody and redaction into a defensible whole.
Tamper-proof audit logs provide the accountability required for audits, discovery, and court review. -
Compliance must be enforced through workflows, not policy alone.
Embedded controls reduce reliance on manual processes and ensure consistent, defensible evidence handling.
Defensible Evidence Is Built, Not Assumed
Digital evidence does not become credible by default. It becomes credible through documented handling, enforced controls, and the ability to prove what happened to that evidence at every stage of its lifecycle. Without these safeguards, even the most critical evidence can be questioned or excluded.
Defensible digital evidence management is built on two non-negotiable capabilities. An unbroken chain of custody ensures that every access, transfer, and modification is recorded and verifiable. Automated redaction ensures sensitive information is protected consistently, without relying on manual processes that introduce risk and delay.
Together, these controls allow organizations to move from basic evidence storage to true evidentiary defensibility. For public safety agencies, legal teams, and regulated enterprises, this means evidence that can withstand courtroom challenge, regulatory scrutiny, and public review when it matters most.
People Also Ask
What makes digital evidence defensible?
Digital evidence is defensible when its handling, integrity, and access can be fully documented and verified through chain of custody and audit trails.
Why is chain of custody important in digital evidence management?
Chain of custody proves that evidence has remained authentic and unaltered from ingestion through use, which is essential for legal and regulatory acceptance.
What is automated redaction in digital evidence?
Automated redaction uses AI to identify and obscure sensitive information in video and audio evidence while maintaining an auditable record.
Why is manual redaction risky for compliance?
Manual redaction is time-consuming and inconsistent, increasing the risk of human error and accidental exposure of sensitive information.
How do audit trails support digital evidence integrity?
Audit trails provide a tamper-proof record of every action taken on evidence, enabling accountability during audits and legal review.
How can organizations prove digital evidence has not been altered?
Organizations rely on cryptographic hashing, access controls, and continuous chain of custody to demonstrate evidence integrity.
How does automated redaction support privacy and disclosure requirements?
Automated redaction protects sensitive information consistently while allowing evidence to be shared or disclosed in compliance with regulations.
Jump to
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
%20(1).webp)
How Auto Transcription Benefits 911 Call Centers for Emergencies
How to redact third-party data in SAR call recordings (without redacting the requester)


No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think